Drzewa przeszukiwań binarnych¶
 Opis problemu¶
Opis problemu¶
Implementation¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 | |
Description implementacji¶
Klasa BST¶
Struktura node¶
- Reprezentuje pojedynczy węzeł drzewa.
- Zawiera trzy pola:
int value: wartość przechowywana w węźle.node *left: wskaźnik na lewego potomka.node *right: wskaźnik na prawego potomka.
Pole root¶
Wskaźnik na korzeń drzewa.
Konstruktor BST()¶
Inicjalizuje drzewo, ustawiając root na pusty wskaźnik (nullptr).
Metoda get_root()¶
Zwraca wskaźnik na korzeń drzewa.
Metoda insert(int value)¶
- Wstawia nową wartość do drzewa.
- Tworzy nowy węzeł z podaną wartością.
- Jeśli drzewo jest puste, nowy węzeł staje się korzeniem.
- W przeciwnym razie, przeszukuje drzewo, aby znaleźć odpowiednie miejsce dla nowego węzła.
Metoda inorder(node *current)¶
Przechodzi przez drzewo w porządku inorder (lewy, korzeń, prawy) i wypisuje wartości węzłów.
Metoda preorder(node *current)¶
Przechodzi przez drzewo w porządku preorder (korzeń, lewy, prawy) i wypisuje wartości węzłów.
Metoda postorder(node *current)¶
Przechodzi przez drzewo w porządku postorder (lewy, prawy, korzeń) i wypisuje wartości węzłów.
Metoda clear(node *current)¶
Rekurencyjnie usuwa wszystkie węzły drzewa, zwalniając pamięć.
Destruktor ~BST()¶
Wywołuje metodę clear, aby usunąć wszystkie węzły i zwolnić pamięć przy niszczeniu obiektu BST.
Funkcja main()¶
- Tworzy tablicę
arrayz wartościami do wstawienia do drzewa. - Tworzy obiekt
BST. - Wstawia wartości z tablicy do drzewa.
- Wypisuje wartości drzewa w trzech różnych porządkach: inorder, preorder i postorder.
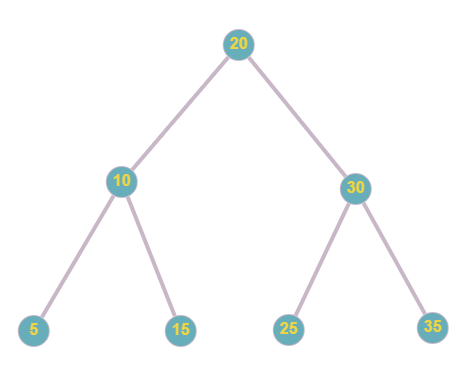
Exampleowe drzewo wykorzystane w implementacji¶